TOTALLY
AWESOME
SCIENCE
PROMISE
PROMISE
Name:
©2020 Sanford Health. All rights reserved. promise.sanfordhealth.org
BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Many rare diseases, cancers, and genetic
conditions can be traced to a mutation in DNA. Although there is research
occurring on how mutations occur, it is known that the leading causes of
mutations are radiation and carcinogens. When DNA is mutated, it disrupts
protein synthesis and causes proteins to be formed incorrectly or not at all.
Proteins are essential for all processes within the cell including regulation of the
cell cycle, cell respiration, metabolism, and synthesis. Through this activity, you
will see how dierent mutations aect proteins.
There are two main categories of mutations. A point mutation occurs when
one nucleotide is changed. For example, an adenine is exchanged for a thymine.
Point mutations can be harmless but can also cause issues in protein formation.
A frameshift mutation occurs when there is either an insertion or deletion of
nucleotides.
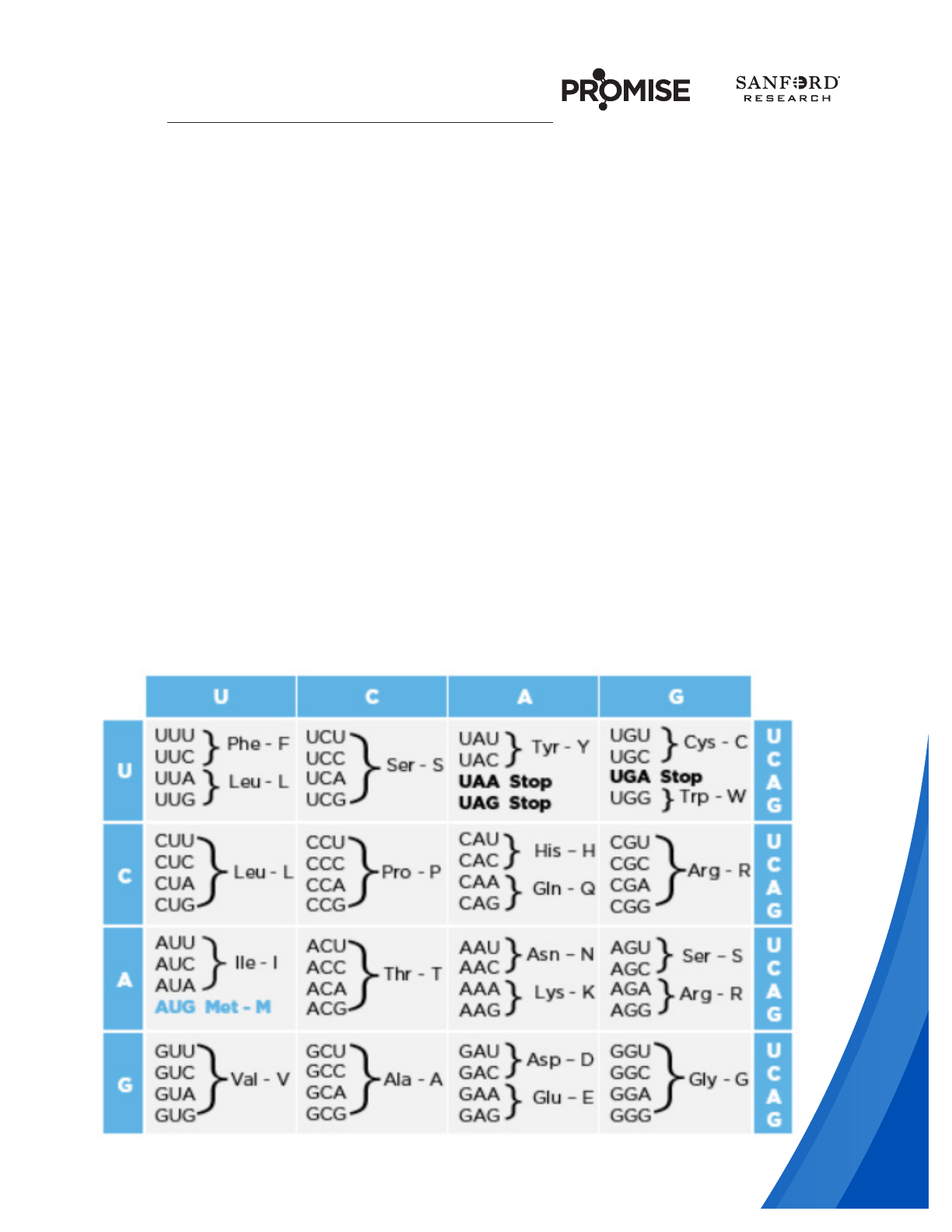
DIRECTIONS: For each sequence of DNA, break the code down into 3-letter
codons. Next, transcribe the DNA code into mRNA code. Finally, use the mRNA
code box below to translate the sequence into a polypeptide of amino acids.
RESEARCH BASICS: DNA MUTATION

TOTALLY
AWESOME
SCIENCE
©2020 Sanford Health. All rights reserved. promise.sanfordhealth.org
DNA
mRNA
TACATAAGAAAGTCACCAGGGCCCCTTTAAGATGACGGGGGCGTTTGAGCACACACT
Each of the following DNA sequences is mutated. Circle or highlight the area
of the DNA that is mutated. Complete transcription and translation on each
sequence and determine the eect on the protein.
Amino
Acids
1. Which type of mutation(s) occurred above?
2. How did the mutation aect the amino acid sequence?
NORMAL DNA
DNA
mRNA
TACATAAGAAAATCACCAGGGCCCCTTTAAGATGACGGGGGCGTTTGAGCACACACT
Amino
Acids

TOTALLY
AWESOME
SCIENCE
©2020 Sanford Health. All rights reserved. promise.sanfordhealth.org
1. Which type of mutation(s) occurred above?
2. How did the mutation aect the amino acid sequence?
DNA
mRNA
TACATAAGAAAATCACCAGCCCCTTTAAGATGACGGGGGCGTTTGAGCACACACT
Amino
Acids
1. Which type of mutation(s) occurred above?
2. How did the mutation aect the amino acid sequence?
DNA
mRNA
TACATAACTAAAGTCACCAGGGCCCCTTTAAGATGACGGGGGCGTTTGAGCACACACT
Amino
Acids
